

Siding on the Exterior InSoFast Panel
Why work harder and pay more?

The real comparison is about material and labor. This is an unfair comparison, InSoFast costs less and is only 20% of the labor. The example we have here is based on a 2,400 sq-ft surface area, a wall that is 120 feet long by 20 feet high. SPOILER ALERT, InSoFast cost less and is 80% faster.
The quick answer: in $$
Traditional method with 80% more parts, more work, and cost $13,523.72
$5.63 per square foot for materials
InSoFast’s single step panel 20% of the work and cost $12,818.43
$5.34 per square foot for materials
For just materials that is a savings of $705.29
Rotten Apples
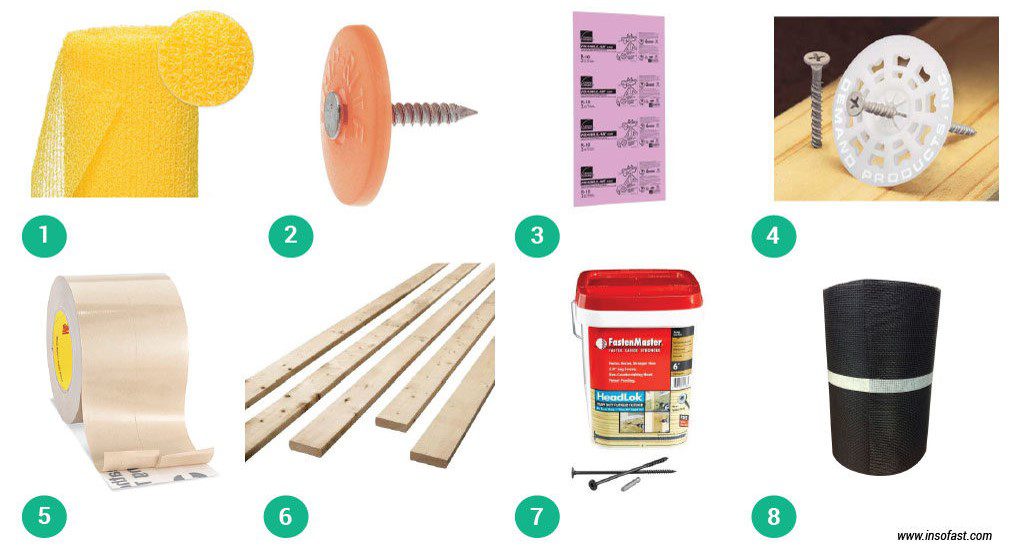

| Product/Link | Description/Purpose | Costs | Quantity | Quantity |
| 1. Slicker® Classic Rainscreen | This is a drainage layer that ensures moisture is able to flow away from the interior of your home. | $196.00 | 16 | $3,136.00 |
| 2. Plastic Cap Roofing Nails | Fasteners required to secure the Slicker® Classic Rainscreen every 3 feet (penetrating the air barrier). | $11.53 | 4 | $46.12 |
| 3. Rigid Foam Insulation | Owens Corning FOAMULAR 250 2 in. x 4 ft. x 8 ft. R-10 Scored Squared Edge Insulation Sheathing | $50.76 | 75 | $3,807.00 |
| 4. Recessed Chamber Fasteners | Specialty fasteners used to secure insulation to the sheathing (penetrating the air barrier). | $330.52 | 1 | $330.52 |
| 5. Foamboard Flashing Tape | TYVEK Tape, final step provides maximum reduction of air infiltration and water protection. | $14.65 | 8 | $117.20 |
| 6. Furring Strip Boards | 1 in. x 3 in. x 8 ft. Eastern White Pine Furring Strip Board *(5/4 in. x 3 in. x 8 ft. Furring Strip Board). | $2.58 | 330 | $851.40 |
| 7. Heavy Duty Fasteners | HeadLok 4-1/2 in. Heavy Duty Flathead Fastener 50 screws per box) (penetrating the air barrier). | $41.98 | 48 | $2,015.04 |
| 8. Cor-a Vent Insect Screen | Rainscreen material to prevent insect infiltration along the top and bottom edge of the insulation. | $8.28 | 30 | $248.40 |
| $10,393.68 |
Juicy Oranges
MAX 3.75 Panel R-15.9 Continuous Insulation
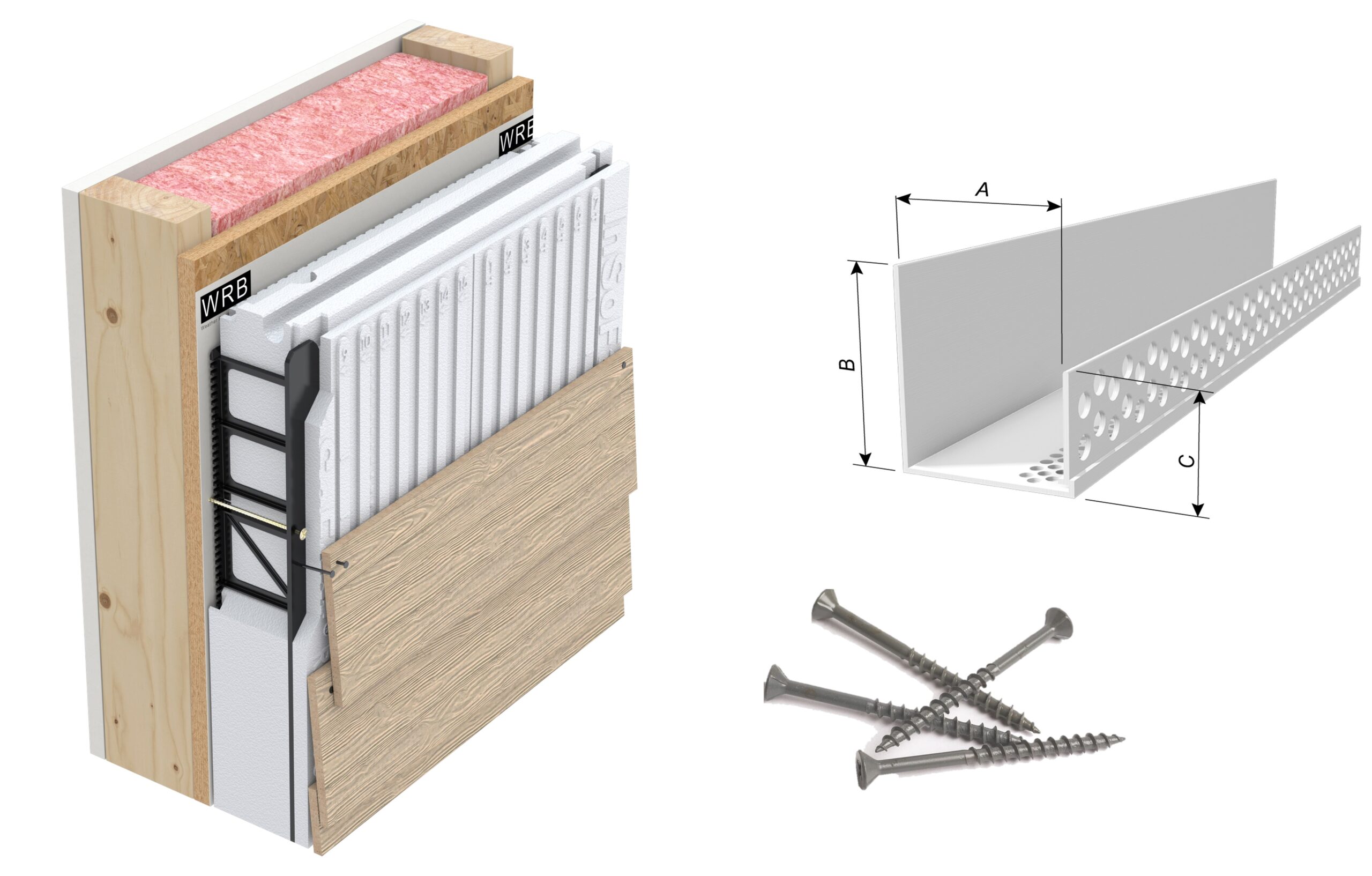
Continuous insulation done right.
| Product/Link | Description/Purpose | Costs | Quantity | Quantity |
| 1. MAX 3.75 | The Max 3.75 R-15.9 panels are an all-in-one solution to the rainscreen/insulation/attachment fiasco above. | $205.00 | 60 | $12,300.00 |
| 2. Starter Track | Serves as a bug screen, provides drainage and a level starter track for the panel installation.* | $16.58 | 15 | $248.70 |
| 3. Wood Screw Fasteners | #10 x 3-1/2 in. Philips Bugle-Head Coarse Thread Polymer Coated Exterior Screws (5 lbs./Pack) | $29.97 | 9 | $269.73 |
| $12,818.43 |
All prices are based on the online sources represented in the hyperlinks below as of May 17th, 2023. (THESE PRICES MAY ALREADY BE OUT OF DATE) you could save even more! The total costs does not reflect additional expenses levied by taxes, shipping or labor.
* Alternate method a coil stock drip cap
We honestly spent a bulk of our time researching the most cost-effective products and places to purchase our competitor’s products for the traditional assembly. Home Depot pricing varies by zip code, so our calculations reflect pricing found local to our office in Reading, PA. If you think you could do better, please feel free to refute our claims and email us corrections!
The Breakdown:
To highlight the differences between InSoFast EX 2.5 panels and Traditional Exterior Wall Assemblies, we compared cost and materials. InSoFast is 1000’s (THOUSANDS OF PARTS LESS ), to handle, manage, order, lose, and then reorder….
Compare InSoFast’s approach to typical construction methods.

Our cost analysis begins where the house wrap, (WRB), or Zip Wall type barrier ends, the exterior sheathing to the outermost finish. For comparison we finish the project with siding because, *using screws to attach the insulation system. Don’t let our choice of siding limit your creativity, both methods support a wide variety of finishes including stone veneer, stucco, brick and more.
*InSoFast can save time and money over load bearing masonry (concrete or block walls) using our patented adhesive attachment method that would not be a fair comparison.

What else are you losing or missing out on, other than profit?
We didn’t engineer our product to be less expensive we engineered it to be better. We focused on eliminating the complex variables that can muck up good intentions. We wanted something simple and effective. A secure, future-ready investment. The overall product cost and labor savings are just a bonus.

